- Related articles
- What 802.3 Standard Originally Defined Poe Functionality?
- Apply to 1000BASE-LX Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-47.72's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-C9336PQ= Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560CG-8TC-S Switch
- What is SFP in Networking?
- All Cisco SFP-10G-LR-S's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- All Cisco DS-SFP-FC8G-ER's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco XENPAK-10GB-LR+'s information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility m
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48TQ-S Switch

Introduction:
In this article, we will briefly introduce the 100BASE-X Ethernet standard and what are the difference between 100BASE-X and 100BASE-T, so that allows viewers to have a more profound understanding for 100BASE-X technology, better to understand the basic solutions to 100BASE-X.
What is the 100BASE-X technology?
The 100BASE-X (Fast Ethernet) standard is an extension of the existing Ethernet standard. It runs on UTP Category 5 data grade cable and uses CSMA/CD in a star wired bus topology, similar to 10BaseT where all cables are attached to a hub.
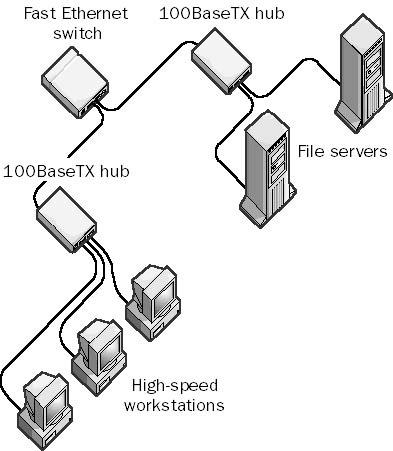
What are the Difference Between 100BASE-X and 100BASE-T?
100BASE-X uses a star bus topology similar to 10BASE-T. 100BASE-X provides a data transmission speed of 100 Mbps using baseband. 100BASE-X is sometimes referred to as “Fast Ethernet.” Like 100VG-AnyLAN, 100BASE-X provides compatibility with existing 10BASE-T systems and thus enables plug-and-play upgrades from 10BASE-T.
A networking standard that supports data transfer rates up to 100 Mbps (100 megabits per second). 100BASE-T is based on the older Ethernet standard. Because it is 10 times faster than Ethernet, it is often referred to as Fast Ethernet. Officially, the 100BASE-T standard is IEEE 802.3u.





































































