- Related articles
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-30.33's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960X-48TS-LL Switch
- What Is GJYXCH Fiber Optic Cable?
- All Cisco CWDM-SFP-1270's information (List price, Specs, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48PQ-E Switch
- Apply to 100Base-LX Standard optical transceiver models
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-C9372PX-E Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SE-2G-S1's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- How does a network interface card work?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-3000-4TC Switch
Recommend tag

What is mode in optical fiber?
Definition:
An optical fiber (or optical fibre) is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in optical fiber communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than wire cables.
Application:
Optical fibers have a wide number of applications. They are used as light guides in medical and other applications where bright light needs to be shone on a target without a clear line-of-sight path. Optical fiber is also used in imaging optics. A coherent bundle of fibers is used, sometimes along with lenses, for a long, thin imaging device called an endoscope, which is used to view objects through a small hole. In spectroscopy, optical fiber bundles transmit light from a spectrometer to a substance that cannot be placed inside the spectrometer itself, in order to analyze its composition. An optical fiber doped with certain rare earth elements such as erbium can be used as the gain medium of a laser or optical amplifier. It is also widely exploited as a nonlinear medium and so many features.
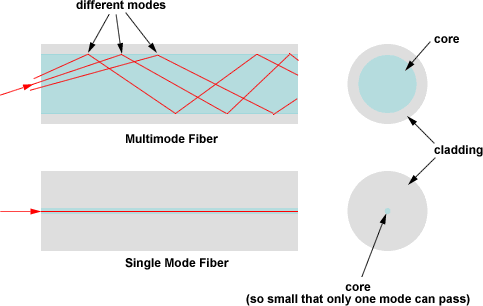
Modes of optical fiber
Single mode fiber
Fiber supporting only one mode is called single-mode or mono-mode fiber. Single-mode fiber allows for a higher capacity to transmit information because it can retain the fidelity of each light pulse over longer distances, and it exhibits no dispersion caused by multiple modes. The most common type of single-mode fiber has a core diameter of 8 to 10 μm. The smaller core diameter makes coupling light into the core more difficult. Data rates of up to 10 gigabits per second are possible at distances of over 60 km with commercially available transceivers.
Multimode fiber
Multimode fiber is best designed for short transmission distances and is suited for use in LAN systems and video surveillance. Modes result from the fact that light will only propagate in the fiber core at discrete angles within the cone of acceptance. Multi-mode fibers have large core diameters and they can support applications from 10 Mbit/s to 10 Gbit/s over link lengths of up to 550 meters, more than sufficient for the majority of premises applications.
Conclusion:
With the increasing use and demand of optical fiber, the development speed and the potential of the optical fiber are enormous. As an important support information technology platform, optical communication technology plays an important role in the future information society. From the development trend of modern communications, the optical fiber communication will become the mainstream of future communication development. People expect all-optical fiber networks will begin to come in the near future.
Please click to check more related concepts:
| Fiber mode | Application |
| Multi-mode | Gigabit Ethernet |

TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Get solutions or consultation from the technical team.