- Related articles
- Overview Cisco GLC-LH-SM Of SFP Transceiver Module
- EoS and EoL Cisco 2960-S Series and 2960-SF Series Switches
- Cisco GBIC Product Line Application
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750G-12S-SD Switch
- All Cisco SFP-OC3-LR2's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matri
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-F24TS-S Switch
- All Cisco XFP-10GER-OC192IR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N3K-C3132Q-XL Switch
- What is 1000BASE T Transceiver?
- What is a DWDM transceiver?
Recommend tag

What is Dark fiber?
2016-07-15
Definition:
A dark fibre (or dark fiber) or unlit fibre is an unused optical fibre, available for use in fibre-optic communication.
What is dark fiber service?
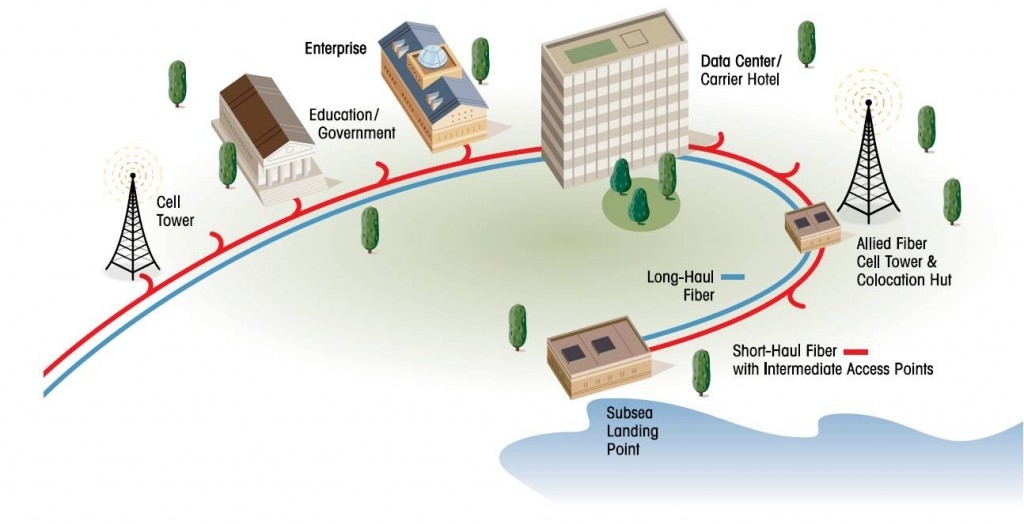
The term dark fiber was originally used when referring to the potential network capacity of telecommunication infrastructure, but now also refers to the increasingly common practice of leasing fibre optic cables from a network service provider, or, generally, to the fibre installations not owned or controlled by traditional carriers. A dark fiber network or simply dark network is a privately operated optical fiber network that is run directly by its operator over dark fibre leased or purchased from another supplier, rather than by purchasing bandwidth or leased line capacity. Dark fibre networks may be used for private networking, or as Internet access or Internet infrastructure networking.
Variations:
Managed dark fiber
Managed dark fiber is a form of wavelength-division multiplexed access to otherwise dark fiber where a simple "pilot" signal is beamed into the fiber by the fiber provider for management purposes using a transponder tuned to the assigned wavelength. DWDM systems generally require central management because their closely spaced wavelengths are subject to disruption by signals on adjacent wavelengths that are not within tightly controlled parameters, especially if amplification is required for signal transmission over 100 km.
Virtual dark fiber
Virtual dark fiber using wavelength multiplexing allows a service provider to offer individual wavelengths ("lambdas" (λ) or "colors"), where access to a dark narrowband wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) optical channel is provided over a wavelength division multiplexed fiber network that is managed at the physical level, but unlit by the network provider. This is typically done using coarse wavelength division multiplexing CWDM because the wider 20 nm spacing of the wave bands makes these systems much less susceptible to interference.
Networks:
Dark fibre can be used to create a privately operated optical fiber network that is run directly by its operator over dark fibre leased or purchased from another supplier, rather than by purchasing bandwidth or leased line capacity. Dark fiber networks may be used for private networking, or as Internet access or Internet infrastructure networking.Dark fiber networks may be point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, or use self-healing ring or mesh topologies. Because there is no intermediate resale of capacity, dark fiber networks can operate using the latest optical protocols using wavelength division multiplexing to add capacity where needed, and to provide an upgrade path between technologies without removing the network from service.For example, many dark fiber metropolitan area networks use cheap Gigabit Ethernet equipment over CWDM, rather than expensive SONET ring systems.
They offer very high price-performance for network users who require high performance, such as Google, which has dark network capacities for video and search data, or wish to operate their own network for security or other commercial reasons.
Conclusion:
However, dark fiber networks are generally only available in high-population-density areas where fibre has already been laid, as the civil engineering costs of installing fibre to new locations is often prohibitive. For these reasons, dark fiber networks are typically run between data centers and other places with existing fiber infrastructure.
Please click to check more concepts:
| Network | Fiber mode |

TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Get solutions or consultation from the technical team.